The Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology Directorate teamed with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory to develop POINTER, groundbreaking first responder tracking technology that uses magnetoquasistatic fields to three-dimensionally locate responders during emergencies—especially when visibility is low due to heavy smoke or debris. With POINTER, incident command can pinpoint team members to within centimeters.
 What are Magnetoquasistatic (MQS) Fields?
What are Magnetoquasistatic (MQS) Fields?
MQS fields are magnetic fields with very slow temporal variations and that appear static, just like the Earth’s magnetic field. MQS fields penetrate most natural materials—as a result, they are used in a broad array of sensor applications, especially where line-of-sight is compromised.
Learn more about MQS fields and how POINTER uses them to locate first responders.
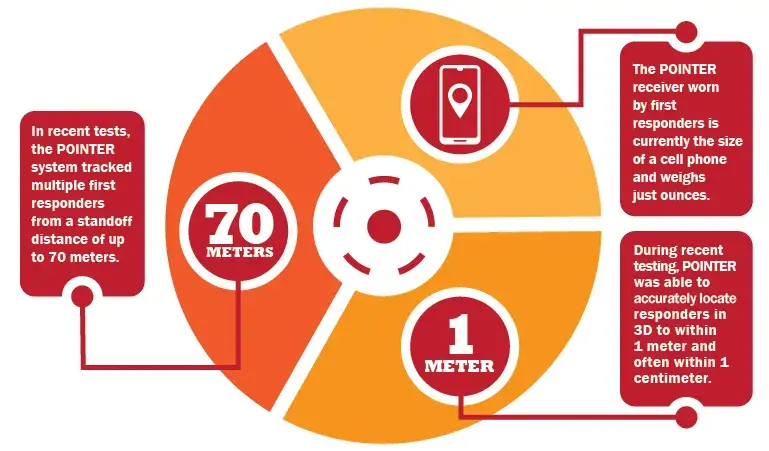

Still want to know more about POINTER?
Let us ‘point’ you in the right direction! Reach out to S&T on social media at @DHSSciTech or contact POINTER@hq.dhs.gov.






